Hepatitis
Hepatitis is a general term used to describe inflammation of the liver
There are several types of viral hepatitis, including:
- Hepatitis A: This is a highly contagious viral infection that is spread through contaminated food or water. Symptoms may include fever, nausea, vomiting, and jaundice.
- Hepatitis B: This is a viral infection that is spread through blood, semen, or other bodily fluids. It can lead to chronic liver disease and liver cancer if left untreated.
- Hepatitis C: This is a viral infection that is spread through blood-to-blood contact. It can also lead to chronic liver disease and liver cancer if left untreated.
Other types of hepatitis include hepatitis D and E, which are less common.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of hepatitis may include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
- Dark urine
- Pale-colored stools
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes)
- Joint pain and muscle aches
- Fever
- Itching
Causes
Hepatitis can have several different causes, including:
- The most common cause of hepatitis is a viral infection. There are five types of viral hepatitis, including hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E.
- Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to alcoholic hepatitis, which is inflammation of the liver caused by alcohol.
- In some cases, the body's immune system can mistakenly attack the liver, leading to autoimmune hepatitis.
- Rare metabolic disorders, such as hemochromatosis and Wilson's disease, can also cause hepatitis by affecting the way the liver functions.
- Exposure to certain toxins, such as industrial chemicals and pesticides, can cause hepatitis.
- Hepatitis can also be caused by other viral infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus or cytomegalovirus.

Diagnosis & Treatment
diagnosisFor viral hepatitis, antiviral medications may be prescribed to help fight the virus and reduce inflammation in the liver. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding alcohol and maintaining a healthy diet, may also be recommended.
For autoimmune hepatitis, treatment typically involves corticosteroids and other immunosuppressive drugs to reduce inflammation and prevent further damage to the liver. In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary.
For alcoholic hepatitis, the first step in treatment is to stop drinking alcohol. Medications may also be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and improve liver function.
In general, early diagnosis and prompt treatment are important for preventing long-term damage to the liver and reducing the risk of complications. of hepatitis typically involves a combination of blood tests and imaging studies
Blood tests can detect the presence of antibodies to specific viruses, as well as measure liver enzyme levels and other markers of liver function. Imaging studies, such as ultrasound or CT scan, can also be used to evaluate the liver for signs of damage or disease.
What to expect after treatment
Here are some general things you can expect after treatment:
1.If you had symptoms related to hepatitis, such as fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, and jaundice, you should experience a reduction in these symptoms as your liver function improves.
2.Treatment can help reduce inflammation and damage to the liver, allowing it to function more effectively.
3.Your doctor will likely schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your condition and ensure that the infection has been fully cleared.
4.In some cases, lifestyle changes may be necessary to prevent further damage to the liver. These may include avoiding alcohol, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
5.Depending on the type of hepatitis you had, regular testing might be recommended to monitor your liver function and screen for any signs of recurring infection.
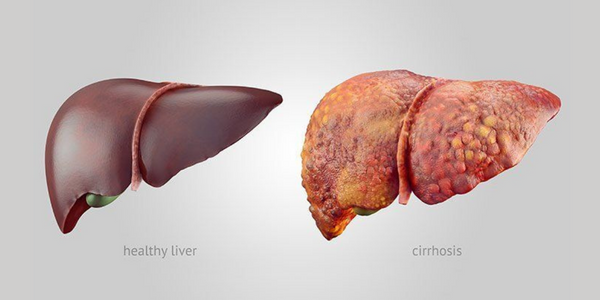
Liver Cirrhosis
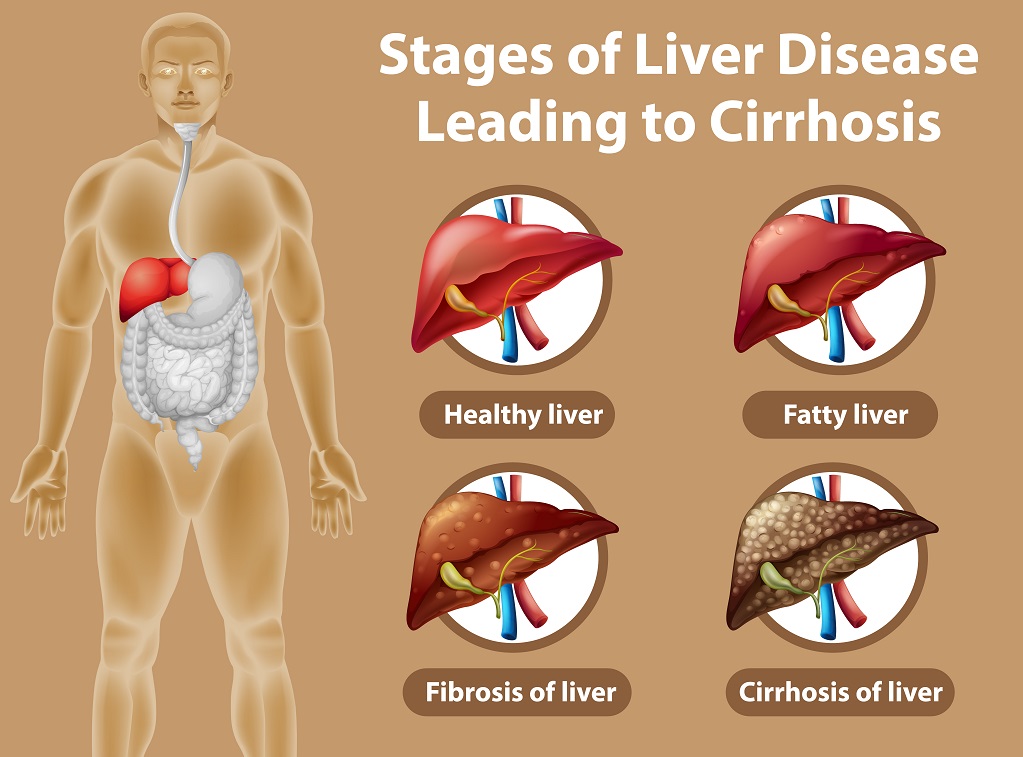
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease characterized by scarring and damage to the liver tissue. This scarring occurs as a result of long-term liver damage, such as from chronic hepatitis, alcohol abuse, or other causes.
As liver tissue becomes damaged, it is replaced by scar tissue, which can block the flow of blood through the liver and impair liver function.
Symptoms
Liver Cirrhosis can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications, including:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Itching
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Swelling in the legs and ankles
- Confusion, memory loss, and other cognitive changes
- Increased risk of infection and bleeding
Causes
Liver cirrhosis is most commonly caused by chronic liver damage from a variety of different conditions, including:
- Chronic alcohol abuse
- Chronic viral hepatitis
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Genetic disorders
- Biliary cirrhosis
Diagnosis & Treatment
The diagnosis of liver cirrhosis is usually made through a combination of physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies, and liver biopsy. The physical examination may reveal a distended abdomen, jaundice, and signs of liver failure. Blood tests may show abnormalities in liver function, while imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT, or MRI may reveal changes in liver texture and size. Liver biopsy may be done to confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of liver damage.
The treatment of liver cirrhosis depends on the cause and severity of the disease. For instance, if the disease is caused by alcohol abuse, the patient needs to stop drinking. If it is caused by hepatitis infection, antiviral medications may be prescribed to control the infection.
Other treatments for liver cirrhosis include medications to reduce the risk of complications such as portal hypertension, variceal bleeding, and ascites. A low-salt diet and diuretics may be prescribed to manage ascites. In severe cases, liver transplantation may be needed to replace the damaged liver with a healthy one.
What to expect after treatment
Here are some things you can expect after liver cirrhosis treatment:
1.Improvement in liver function
2.Reduced risk of complications
3.You may need to make certain lifestyle changes to manage your condition better. This may include a low-salt diet, regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol and drugs that can harm your liver.
4.You may need monitoring after treatment to ensure that your liver is functioning correctly and that there are no signs of relapse.
5.Medications and other treatments will be prescribed for long term care to manage your symptoms and prevent complications.
6.Liver transplantation: In severe cases where the liver is severely damaged, liver transplantation may be necessary to replace the damaged liver with a healthy one.

Liver Abscess
A liver abscess is a collection of pus in the liver tissue, usually caused by a bacterial infection. It is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a liver abscess can vary but may include fever, chills, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and jaundice. In some cases, there may be no symptoms at all.
Causes
The most common causes of liver abscess include infections that spread to the liver from other parts of the body, such as the abdomen, intestines, or biliary tract. It can also occur due to trauma or surgery in the liver, or as a complication of other conditions such as diabetes or liver cirrhosis.

Diagnosis & Treatment
The diagnosis and treatment of liver abscess involves several steps to ensure prompt and effective management of the condition.
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Imaging studies
- Biopsy
Treatment:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are the primary treatment for liver abscesses caused by bacterial infections.
- Drainage: In addition to antibiotics, the abscess may need to be drained to remove the pus and reduce the risk of complications. This can be done through needle aspiration, where a needle is inserted into the abscess to remove the pus, or through surgical drainage.
- Pain management: Pain management medications may be prescribed to manage the pain associated with the abscess.
- Nutritional support: Nutritional support, including adequate hydration and nutrition, may be necessary to support the immune system and help the body fight the infection.
- Follow-up care: Follow-up care is essential to ensure that the abscess has completely healed and to monitor for any signs of relapse or complications.
What to expect after treatment
Here are some general things you can expect after treatment:
1.With successful treatment, the symptoms of liver abscess, such as fever, abdominal pain, and nausea, will gradually improve.
2.After treatment, the liver function will be monitored to ensure that it has returned to normal.
3.It's essential to follow up to monitor your condition and ensure that the infection has completely resolved.
4.Certain lifestyle changes will be recommended to help prevent a recurrence.
5.In some cases, liver abscess can lead to complications such as sepsis, liver failure, or other organ damage.
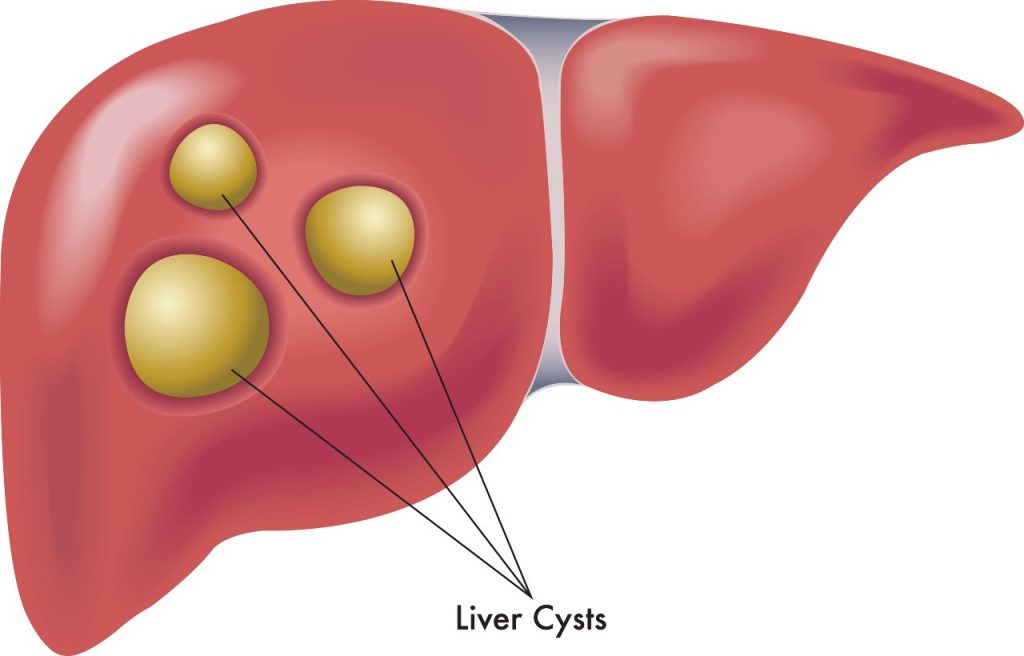
Liver Cysts
Liver cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop in the liver tissue. These cysts can be single or multiple, small or large, and may be present without causing any symptoms. They can develop anywhere in the liver, and their size can vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
Most liver cysts are benign and do not require any treatment. However, in some cases, they can grow large enough to cause discomfort, pain, or other symptoms.
Symptoms
Some of the symptoms of liver cysts may include:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Feeling full or bloated
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Jaundice
- Fever
- Palpable mass in the abdomen
Causes
The causes of liver cysts can be classified into two categories:
- Trauma or injury to the liver
- Infection or inflammation of the liver
- Obstruction of the bile ducts
- Parasitic infections such as echinococcosis
- Exposure to toxins or chemicals
- Long-term use of certain medications such as birth control pills or steroids
Congenital liver cysts: These cysts are present at birth and may be caused by abnormal cell growth during fetal development. Congenital liver cysts can be associated with genetic conditions such as autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, and Caroli disease.
Acquired liver cysts: These cysts develop later in life and can be caused by a variety of factors, including:

Diagnosis & Treatment
Diagnosis of liver cysts usually involves imaging studies such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI. These tests can help determine the size, location, and number of liver cysts present. Blood tests may also be performed to check liver function and rule out other underlying liver diseases.
Treatment options for liver cysts include:
- Aspiration or drainage: This procedure involves using a needle to drain the fluid from the cyst. It is usually performed under ultrasound or CT guidance and may be done for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
- Sclerotherapy: This procedure involves injecting a sclerosing agent into the cyst to shrink it.
- Surgical removal: In rare cases, surgical removal of the cyst may be necessary, especially if the cyst is causing severe symptoms or complications.
- Observation: If the cyst is small and asymptomatic, observation may be the best course of action.
What to expect after treatment
The outcome after treatment of liver cysts is usually good, and most patients experience significant relief from symptoms or complicationsIf the cyst was drained or aspirated, patients can expect to recover within a few days. The procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis, and most patients can resume normal activities within a week.If sclerotherapy was used, patients may experience some discomfort or pain at the injection site, but this typically resolves within a few days. The sclerosing agent causes inflammation and scarring of the cyst, which may take several weeks to resolve completely
If surgical removal was necessary, the recovery time may be longer, depending on the size and complexity of the surgery. Patients may experience some pain and discomfort after the surgery, but pain medications can help manage these symptoms. Overall, the prognosis for liver cysts is excellent, and most patients can expect a full recovery after treatment

Live cancer
Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, is a type of cancer that starts in the cells of the liver. The liver is an essential organ responsible for producing bile to aid in digestion, storing glycogen for energy, and filtering toxins from the blood. Liver cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the liver grow and multiply uncontrollably, eventually forming a mass or tumor.
There are two main types of liver cancer: primary and secondary. Primary liver cancer is cancer that originates in the liver cells, while secondary liver cancer is cancer that has spread to the liver from other parts of the body.
The most common type of primary liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which starts in the main type of liver cells called hepatocytes. Other types of primary liver cancer include intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, which are less common.
Causes
- Chronic infection with hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus can cause inflammation in the liver that can eventually lead to liver cancer.
- Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can damage the liver, leading to cirrhosis and an increased risk of liver cancer.
- People with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) have a higher risk of developing liver cancer
- Obesity and being overweight are risk factors for liver cancer
- Exposure to certain toxins and chemicals can increase the risk of liver cancer.
- Certain inherited conditions, such as hemochromatosis and Wilson's disease, can increase the risk of liver cancer.

Diagnosis & Treatment
Diagnosis of liver cancer typically involves a combination of medical history and physical examination, blood tests, and imaging tests. A liver biopsy may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type and stage of the cancer.
Treatment for liver cancer depends on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health.
Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: Surgery to remove the tumor and a portion of healthy liver tissue is often the first-line treatment for liver cancer if the cancer is confined to the liver and the patient's liver function is good enough.
- Liver transplant: In some cases, a liver transplant may be recommended for patients with early-stage liver cancer that has not spread outside the liver.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells. It may be used to shrink tumors before surgery, to kill any remaining cancer cells after surgery, or to relieve symptoms in advanced liver cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It may be given orally or intravenously and may be used in combination with other treatments.
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy drugs are designed to attack specific proteins or pathways that are involved in cancer growth. They may be used in combination with other treatments.
What to expect after treatment
The recovery process after liver cancer treatment can vary depending on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the treatment approach used.
Surgery: After liver cancer surgery, patients typically spend several days in the hospital and may experience some pain and discomfort for several weeks as they recover. Patients may need to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activity for several weeks after surgery.
Liver transplant: After a liver transplant, patients will need to take medication to prevent their body from rejecting the new liver. These medications can have side effects.
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy: After radiation therapy or chemotherapy, patients may experience fatigue, nausea, and other side effects..
Targeted therapy: After targeted therapy, patients may experience side effects such as fatigue, diarrhea, and rash.
Regardless of the type of treatment used, patients will need regular follow-up appointments to monitor their liver function and check for any signs of recurrence. Patients may also be advised to make lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol and tobacco use to help prevent the recurrence of liver cancer.
