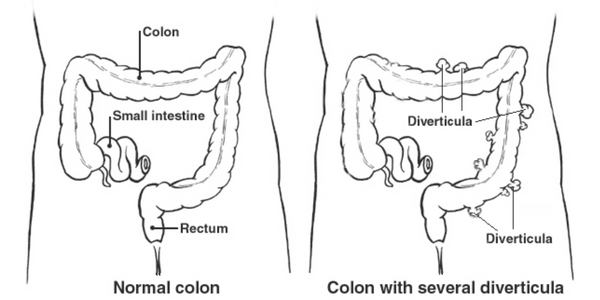
Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is a condition in which small, bulging pouches (diverticula) in the colon become inflamed or infected. These pouches can develop in weak spots in the colon wall, particularly in areas where blood vessels enter the colon. Diverticulitis occurs when one or more of these diverticula become infected or inflamed, causing abdominal pain, fever, and other symptoms.
Diverticulitis can be acute or chronic. Acute diverticulitis is a sudden inflammation of one or more diverticula, while chronic diverticulitis involves repeated episodes of inflammation and infection.
Symptoms
The symptoms of diverticulitis may include:
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Bloating and gas
- Rectal bleeding
- Urinary symptoms
Causes
Diverticulitis is caused by a combination of factors, including:
- A low-fiber diet: A diet that is low in fiber can cause constipation and straining during bowel movements, which can increase pressure in the colon and lead to the formation of diverticula.
- Age: Diverticulitis is more common in people over the age of 50, as the colon becomes weaker with age and is more prone to developing diverticula.
- Genetics: Some people may be more prone to developing diverticula due to genetic factors.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing diverticulitis.
- Lack of exercise: A sedentary lifestyle can also increase the risk of developing diverticulitis.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing diverticulitis.
- Certain medications: Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can increase the risk of diverticulitis.
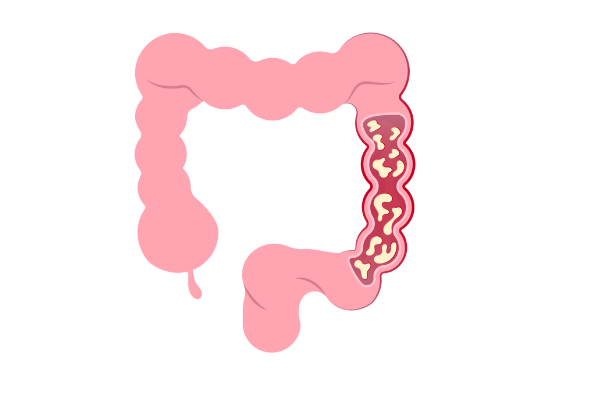
Diagnosis & Treatment
The diagnosis of diverticulitis typically involves a combination of a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. Common diagnostic tests include:
- CT scan
- Blood tests
- Stool tests
Once diagnosed, treatment for diverticulitis may include:
- Antibiotics
- Pain relief
- Rest
- Fiber supplements
- Surgery
What to expect after treatment
After treatment of diverticulitis, most people can expect to gradually return to their normal activities and dietHere are some general expectations:
1.After a period of resting the digestive system with a liquid diet, a gradual reintroduction of fiber is typically recommended to prevent future episodes of diverticulitis.
2.It's important to gradually return to physical activity after diverticulitis treatment, especially if surgery was involved.
3.If antibiotics were prescribed, it's important to complete the entire course as directed by your healthcare provider.
4.Follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider will likely be recommended to monitor progress and ensure that symptoms have resolved.
5.To prevent future episodes of diverticulitis, it's important to maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, stay hydrated, and avoid smoking.
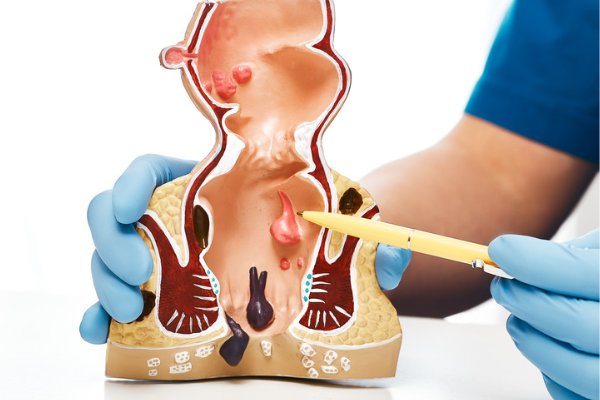
Piles/Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen veins in the lower part of the rectum and anus. Hemorrhoids can be internal or external, depending on their location.
Internal hemorrhoids occur inside the rectum and are usually painless, although they can cause bleeding during bowel movements. External hemorrhoids, on the other hand, occur around the anus and can be painful, itchy, and may bleed.
Symptoms
The symptoms of hemorrhoids, also known as piles, can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Here are some common symptoms:
- Pain or discomfort around the anus
- Anal itching
- Bleeding during bowel movements
- Mucus discharge
- Swelling or lumps around the anus
- Inability to control bowel movements
Causes
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, can be caused by several factors, including:
- Straining to pass stool can put pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus, leading to hemorrhoids.
- Constipation can make it difficult to pass stool, leading to straining and increased pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus.
- During pregnancy, the growing uterus can put pressure on the veins in the pelvis, leading to hemorrhoids.
- Being overweight or obese can increase the pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus, increasing the risk of hemorrhoids.
- Prolonged sitting or standing can increase the pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus.
- Hemorrhoids may run in families, suggesting a genetic component to the condition.
- As people age, the tissues in the rectum and anus may weaken, increasing the risk of hemorrhoids.
- Chronic diarrhea can irritate the rectum and anus, leading to hemorrhoids.
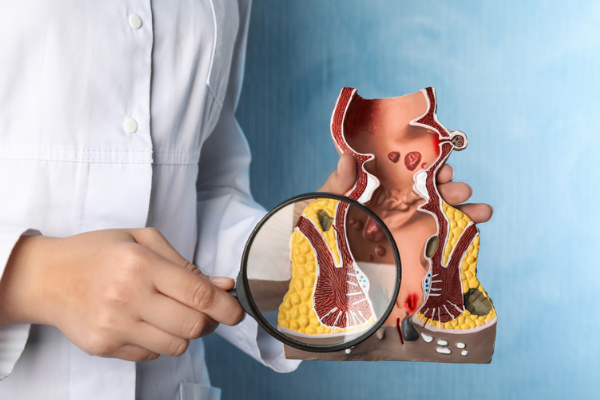
Diagnosis & Treatment
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids usually involves a physical exam of the anus and rectum by a healthcare provider. In some cases, additional tests such as a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy may be necessary to rule out other conditions.
Treatment of hemorrhoids depends on the severity of the conditionHere are some treatment options:
- Lifestyle modifications: Increasing fiber intake, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding straining during bowel movements can help prevent and treat hemorrhoids.
- Topical treatments: Over-the-counter creams, ointments, and suppositories can provide relief from hemorrhoid symptoms, such as itching and pain.
- Sitz baths: Sitting in warm water for 10 to 15 minutes several times a day can help soothe hemorrhoid symptoms.
- Rubber band ligation: A healthcare provider can place a small rubber band around the base of an internal hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply, causing it to shrink and fall off.
- Infrared coagulation: A healthcare provider can use infrared light to shrink internal hemorrhoids.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: In severe cases, a surgical procedure to remove hemorrhoids may be necessary.
What to expect after treatment
After treatment of hemorrhoids, the symptoms should gradually improve over time. You may experience some discomfort or pain in the anus or rectum for a few days if a procedure to remove the hemorrhoids, such as rubber band ligation or hemorrhoidectomy is performed
In general, it's important to maintain good bowel habits, such as avoiding straining during bowel movements, drinking plenty of water, and eating a high-fiber diet to prevent the recurrence of hemorrhoids.
Anal Fistula
An anal fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway that forms between the anus or rectum and the skin surrounding the anus. It is usually the result of an infection in an anal gland that spreads to the skin, causing a small tunnel or channel to form.
Symptoms
Symptoms of an anal fistula can include:
- Persistent pain or discomfort around the anus
- Swelling or redness around the anus
- Itching or irritation around the anus
- Drainage of pus or blood from the opening around the anus
- Painful bowel movements
Causes
Anal fistulas are usually caused by an infection in an anal gland that spreads to the surrounding skin, leading to the development of an abscess. Over time, the abscess can create a tunnel or channel (the fistula) between the anal gland and the skin, which can cause persistent pain and discomfort.
A few risk factors which increase the chances of developing a fistula:
- Crohn's disease or other inflammatory bowel diseases
- Prior abscesses or infections in the anal area
- Anorectal trauma or injury
- A history of anal surgery or procedures
- Certain infections, such as tuberculosis or sexually transmitted infections

Diagnosis & Treatment
Diagnosis of an anal fistula usually involves a physical exam of the anus and rectum by a healthcare provider. In some cases, imaging tests such as an ultrasound or MRI may be necessary to evaluate the extent and location of the fistulaTreatment for an anal fistula typically involves surgery to remove the affected tissue and close the opening or passageway.
Some common surgical options include:
- Fistulotomy: This involves cutting open the fistula and allowing it to heal from the inside out.
- Seton placement: A seton is a thin piece of surgical thread that is inserted through the fistula to keep it open and allow it to drain.
- Advancement flap procedures: This involves using tissue from the rectal wall to close the opening of the fistula.
- Fibrin glue injection: A medical adhesive is injected into the fistula tract to seal it shut.
- Laser surgery: This uses a laser to remove the fistula
What to expect after treatment
After treatment of an anal fistula, the healing process can take several weeks to several months.Immediately after surgery, you may experience some pain, swelling, or discomfort in the anal area. You may be prescribed pain medication or suggested over-the-counter pain relief to help manage these symptoms. You may also need to follow a special diet to help promote healing and prevent constipation.
It's important to avoid activities that could put stress on the anal area, such as heavy lifting or strenuous exercise. You may also need to take time off from work or other daily activities to allow your body to heal.
Overall, with appropriate treatment and self-care measures, most people can expect to make a full recovery from an anal fistula and resume their normal activities.
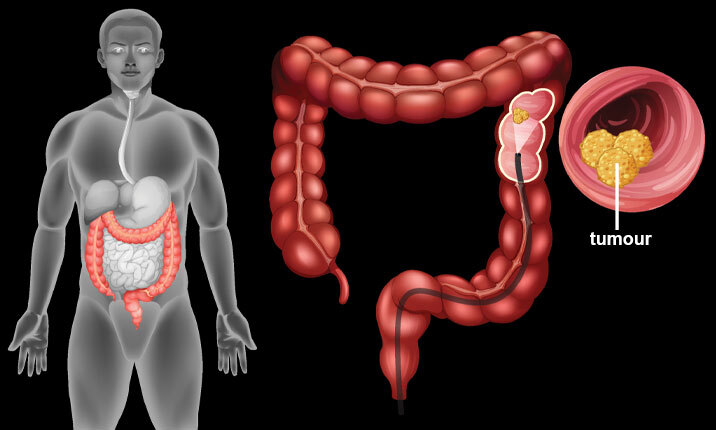
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer, also known as bowel cancer, is a type of cancer that starts in the colon or rectum, which are parts of the digestive system. Colorectal cancer develops when abnormal cells in the lining of the colon or rectum grow uncontrollably, forming a mass of tissue called a tumor. Over time, the cancer can spread to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, liver, or lungs.
Symptoms
Some common signs and symptoms of colorectal cancer include:
- Changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation that lasts for more than a few days.
- Blood in the stool or rectal bleeding
- Abdominal pain, cramping, or discomfort.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Fatigue or weakness.
- Narrow stools.
- Feeling like you need to have a bowel movement that is not relieved by doing so.
- Rectal pain or discomfort.
- Anemia, which can cause fatigue, shortness of breath, and weakness.
Causes
Some of the common risk factors for colorectal cancer include:
- The risk of developing colorectal cancer increases with age. Most people who develop the disease are over the age of 50.
- A family history of colorectal cancer or polyps can increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Individuals who have had polyps or colorectal cancer in the past are at increased risk of developing the disease again.
- Long-standing IBD, such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease, increases the risk of colorectal cancer.
- A diet that is high in red and processed meat, and low in fiber, fruits, and vegetables, can increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Lack of physical activity can increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing colorectal cancer.
- Smoking cigarettes or using other tobacco products can increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
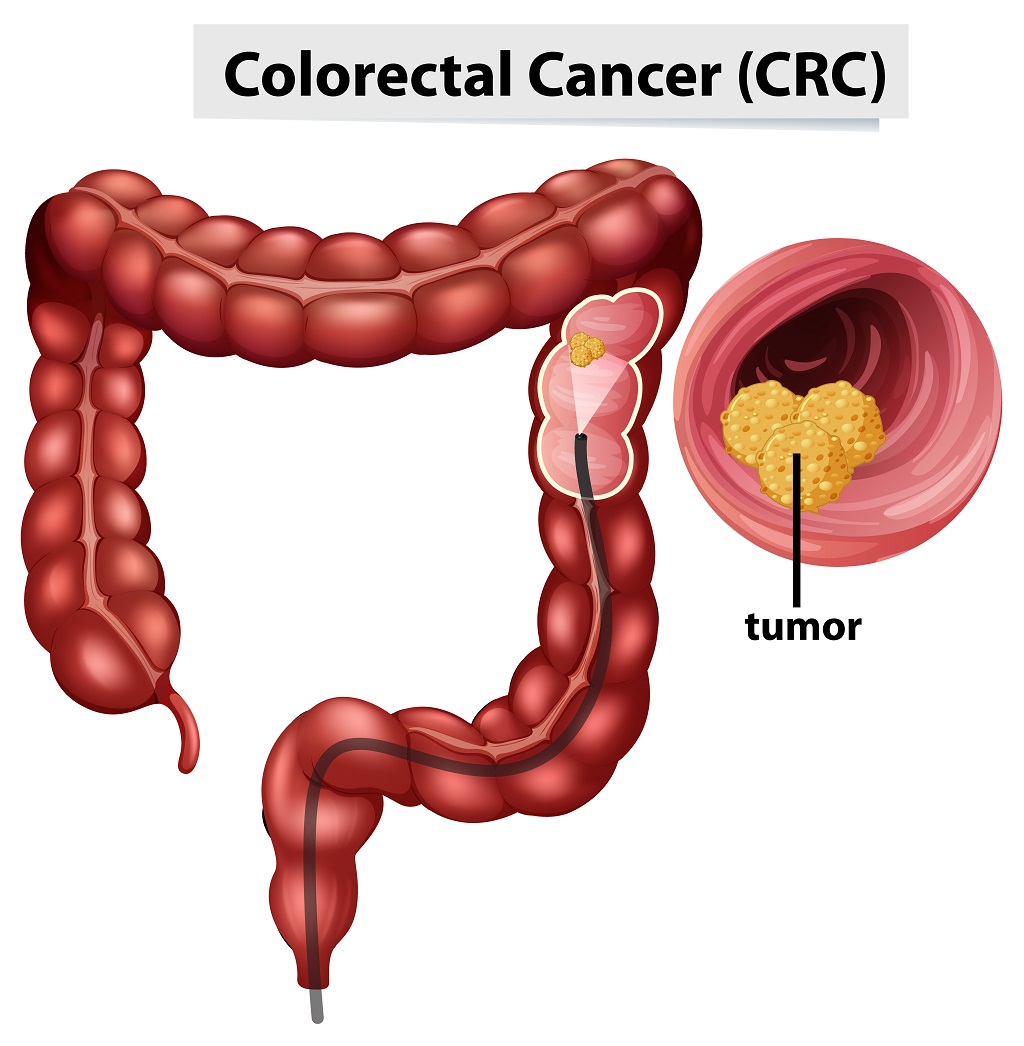
Diagnosis & Treatment
Diagnosis of colorectal cancer usually involves several tests, including:
- Colonoscopy
- Biopsy
- Imaging tests
Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for most cases of colorectal cancer involves surgery to remove the cancerous tissue and surrounding healthy tissue.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy radiation is used to kill cancer cells, either before surgery to shrink the tumor or after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Medications are used to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs are used to target specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy: Drugs are used to help the body's immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
The type of treatment recommended will depend on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the location of the cancer, the patient's overall health, and other factors
What to expect after treatment
here are some common things you may expect after colorectal cancer treatment:
1.follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery and check for any signs of cancer recurrence.
2.You may experience side effects from treatment such as fatigue, pain, diarrhea, constipation, or changes in appetite.
3.changes to your diet and exercise habits is recommended to improve your overall health and reduce your risk of cancer recurrence.
4.Dealing with cancer and its treatment can be emotionally challenging.
5.There is a risk of colorectal cancer recurrence even after successful treatment.

Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes chronic inflammation and ulcers in the innermost lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum. This condition affects the colon and rectum only, and not other parts of the digestive system.
Ulcerative colitis is believed to be an autoimmune disease, in which the body's immune system attacks the healthy tissues of the colon, causing inflammation, swelling, and ulcers.
Symptoms
Some common symptoms of ulcerative colitis are:
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Rectal bleeding
- Urgency to defecate
- Tenesmus
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Joint pain
Causes
Causes of ulcerative colitis are thought to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
Some of the potential causes and risk factors for ulcerative colitis include:
- Research has shown that people with a family history of inflammatory bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis, are at higher risk of developing the condition.
- Certain environmental factors such as diet, stress, and infections may trigger ulcerative colitis in people who are genetically predisposed to the disease.
- Ulcerative colitis is believed to be an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the colon and rectum, causing inflammation.
- Changes in the gut microbiome, which includes the trillions of bacteria that live in the digestive tract, may play a role in the development of ulcerative colitis.
Diagnosis & Treatment
Diagnosis of ulcerative colitis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, stool tests, imaging tests, and endoscopic procedures. The most accurate method for diagnosing ulcerative colitis is through a colonoscopy and biopsy.
Treatment of ulcerative colitis usually involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications.
Medications commonly used to treat ulcerative colitis include:
- Aminosalicylates (5-ASA): These medications are anti-inflammatory drugs that help reduce inflammation in the lining of the colon.
- Corticosteroids: These medications are more powerful anti-inflammatory drugs that are used to reduce inflammation during flare-ups.
- Immunomodulators: These medications suppress the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent flare-ups
- Biologics: These medications target specific proteins in the immune system that are involved in inflammation.
- Antibiotics: These medications are sometimes used to treat infections that may trigger or worsen ulcerative colitis.
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes such as stress management, regular exercise, and a healthy diet may also help manage symptoms of ulcerative colitis.
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected portion of the colon.
What to expect after treatment
here are some general expectations:
1.With effective treatment, symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and rectal bleeding should improve or disappear altogether.
2.As symptoms subside, patients should be able to resume their normal activities and enjoy a better quality of life.
3.Even if symptoms have improved, patients with Ulcerative Colitis will still need to be monitored regularly by a gastroenterologist to ensure that the disease remains under control.
4.Some patients may need to adjust their medication dosages or switch to a different medication if their symptoms do not improve with the initial treatment.
5.Even with successful treatment, there is still a risk of disease flare-ups.
6.In severe cases of Ulcerative Colitis, surgery may be necessary to remove the colon.
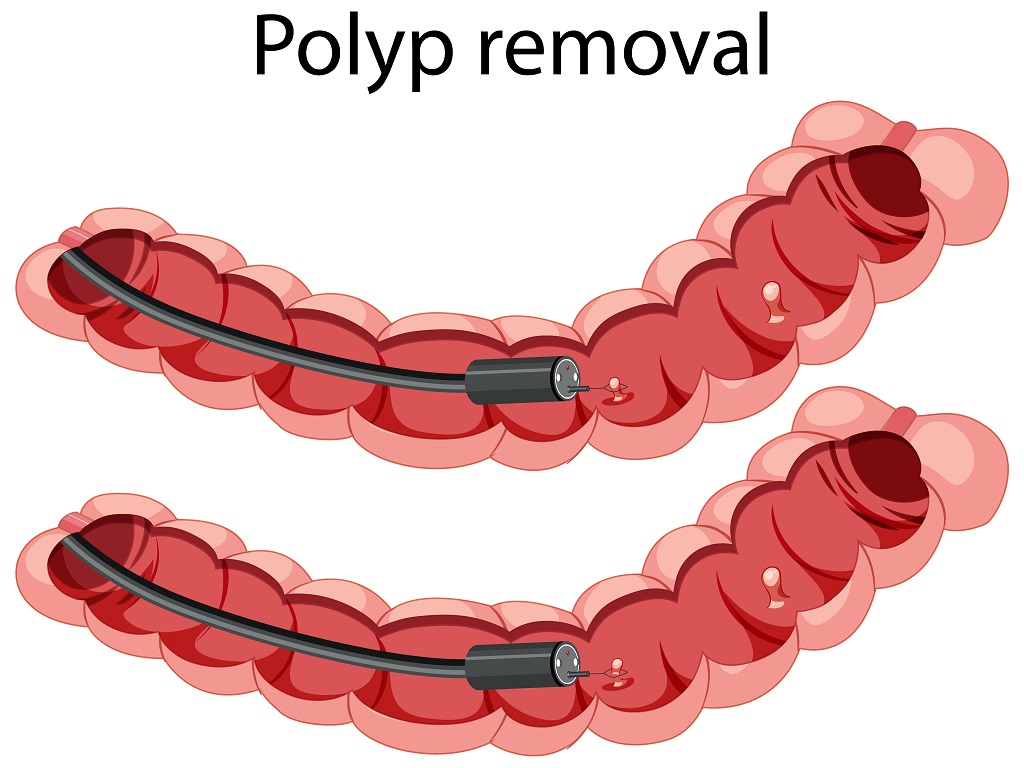
Polyps
Polyps are abnormal growths that can occur in different parts of the body. In the context of gastrointestinal health, polyps are growths that occur in the lining of the colon or rectum. They can vary in size and shape, and can be raised or flat.
Polyps are usually non-cancerous but some types can develop into cancer over time if left untreated.
Symptoms
as polyps grow larger or become more numerous, they can sometimes cause the following symptoms:
- Rectal bleeding
- Changes in bowel habits
- Obstruction
- Anemia
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
Causes
Here are some of the potential causes of polyps in the colon and rectum:
- Polyps are more common in people over the age of 50.
- Having a family history of colon polyps or colon cancer increases the risk of developing polyps.
- People with conditions such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease have a higher risk of developing polyps.
- Factors such as a diet high in red meat and low in fiber, lack of physical activity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of polyps.
- Rare genetic conditions such as Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) and Lynch syndrome can significantly increase the risk of developing polyps.
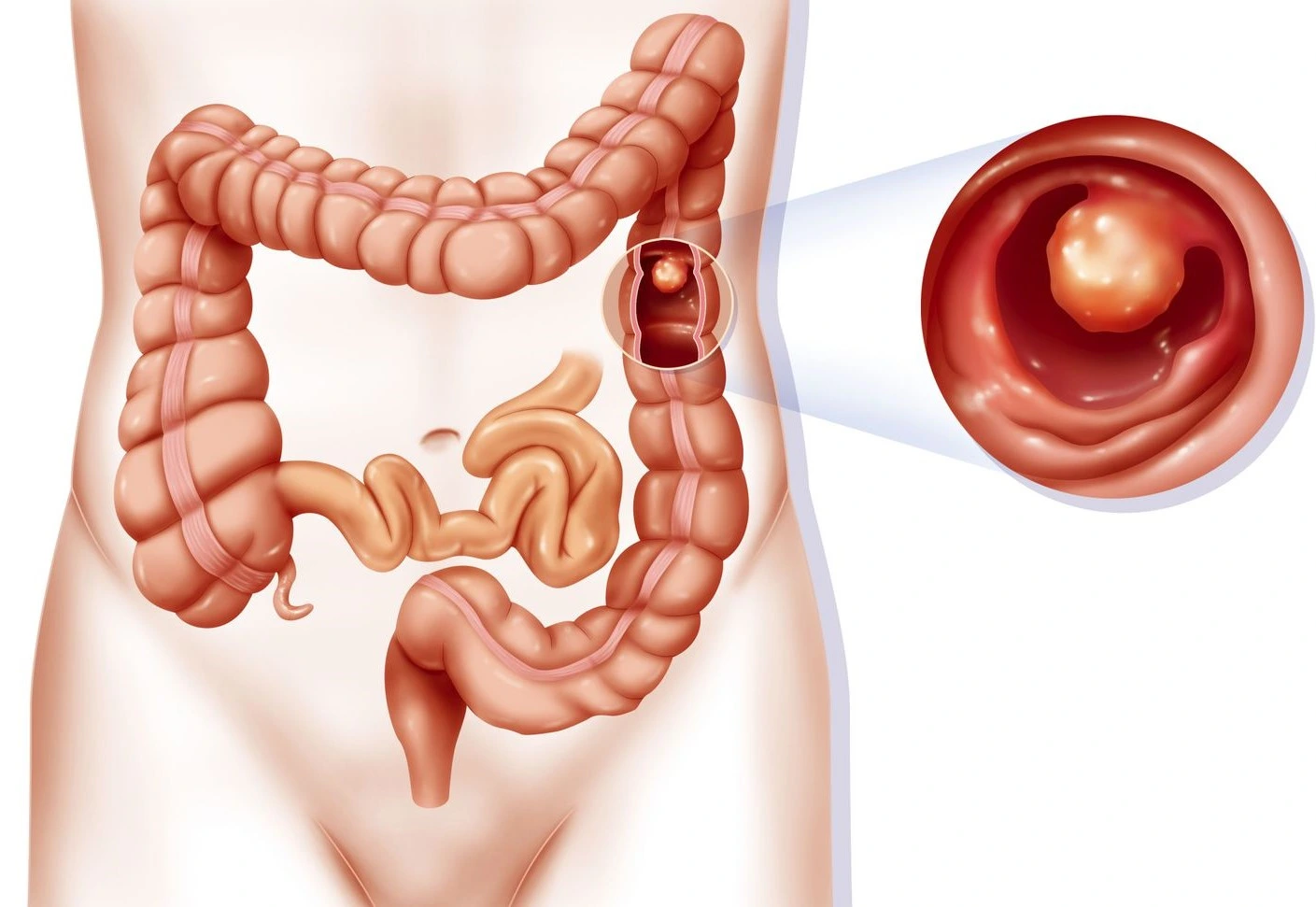
Diagnosis & Treatment
The diagnosis of polyps in the colon and rectum typically involves a colonoscopy. During the colonoscopy, the lining of the colon and rectum can be seen to identify if any polyps that may be present. If a polyp is identified, a biopsy may be taken to determine whether it is cancerous or benign.
Small polyps that are not causing any symptoms may not require treatment, but larger polyps or those that are causing symptoms may need to be removed. This can be done during a colonoscopy by using a snare to cut the polyp from the lining of the colon or rectum. The removed polyp is then sent to a lab for analysis to determine whether it is cancerous or not.
If the polyp is found to be cancerous, further treatment may be necessary, such as surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors.
Prevention of polyps is an important aspect of treatment. This can be achieved through lifestyle modifications such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption. Regular screenings, such as colonoscopies, are also important for the early detection and removal of polyps before they have a chance to develop into cancer.
What to expect after treatment
here are some things you can expect:
1.If the polyps were causing symptoms such as nasal congestion, sinus pressure, or headaches, you should experience relief from these symptoms after treatment.
2.follow-up appointments to monitor your condition will be required to ensure that the polyps do not recur.
3.Medication may be prescribed to help prevent the polyps from coming back.
4.Making certain lifestyle changes, such as avoiding irritants or allergens, may help prevent polyps from returning.
5.If you have had surgery, you may need a few days to recover before returning to normal activities.

